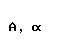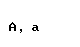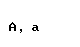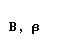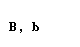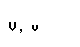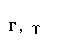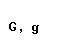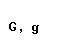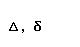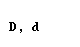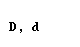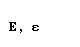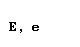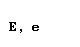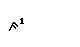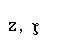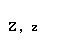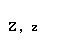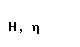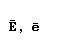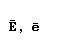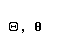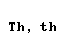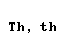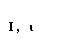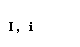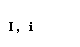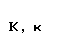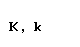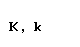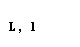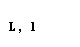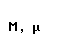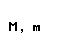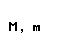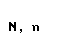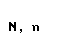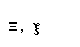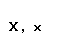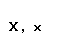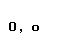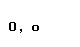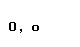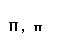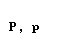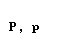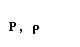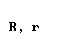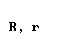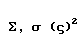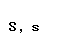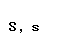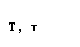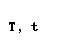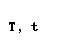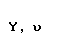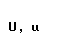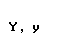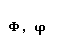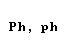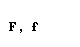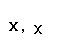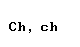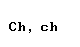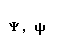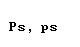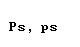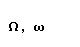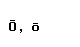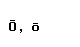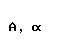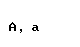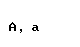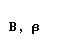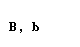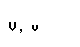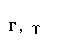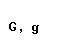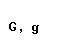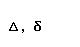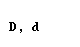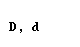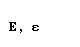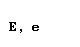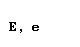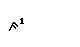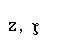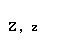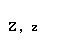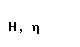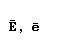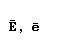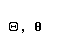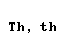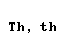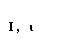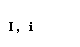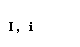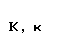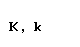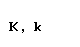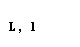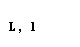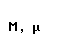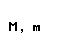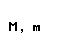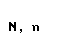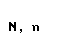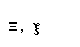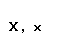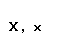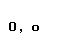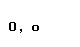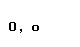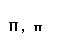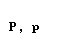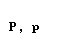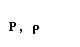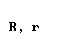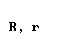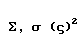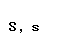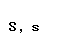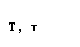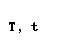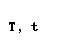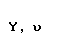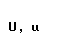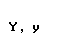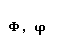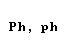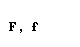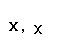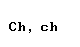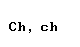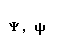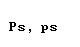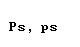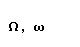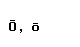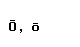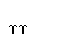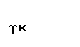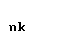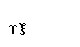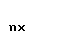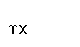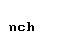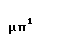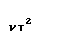The Greek alphabet
| Greek letter | English name | Romanization (Classical Greek) | Romanization (Modern Greek) |
|---|
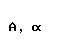 | alpha | 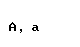 | 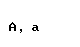 |
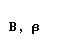 | beta | 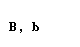 | 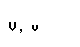 |
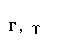 | gamma | 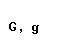 | 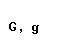 |
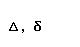 | delta | 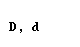 | 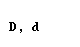 |
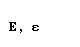 | epsilon | 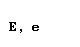 | 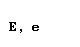 |
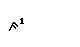 | digamma | N/A | N/A |
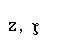 | zeta | 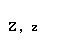 | 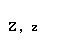 |
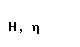 | eta | 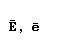 | 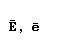 |
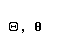 | theta | 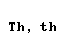 | 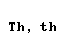 |
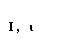 | iota | 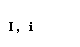 | 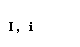 |
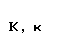 | kappa | 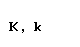 | 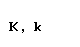 |
 | lambda | 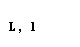 | 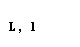 |
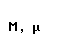 | mu | 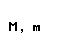 | 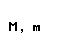 |
 | nu | 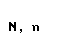 | 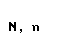 |
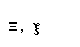 | xi | 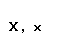 | 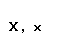 |
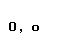 | omicron | 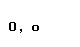 | 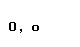 |
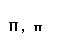 | pi | 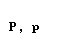 | 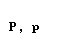 |
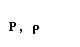 | rho | 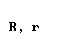 | 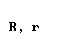 |
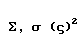 | sigma | 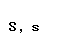 | 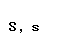 |
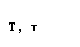 | tau | 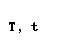 | 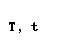 |
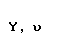 | upsilon | 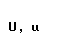 | 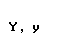 |
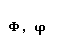 | phi | 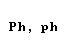 | 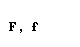 |
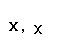 | chi | 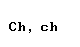 | 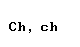 |
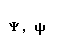 | psi | 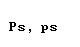 | 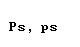 |
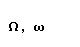 | omega | 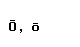 | 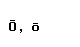 |
1 The digamma represented in ancient Greek the sound of the
letter w in English. This sound later disappeared and consequently the
digamma was dropped from the alphabet.
2 Used at the end of a word.
When certain letters are combined the resulting combination is romanized in a
special way.
| Greek letters | Romanization |
|---|
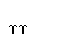 | 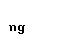 |
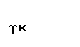 | 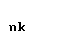 |
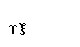 | 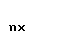 |
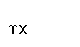 | 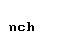 |
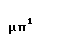 |  |
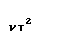 |  |
1The normal romanization is mp. The special form is only
used if the combination of mu and pi in Modern Greek represents
the B sound in loanwords and foreign proper names (The letter
beta is pronounced as English V in modern Greek).
2The normal romanization is nt. The special form is only
used if the combination of nu and tau in Modern Greek
represents the D sound in loanwords and foreign proper names (The
letter delta is pronounced as English TH in the in
Modern Greek).